习题一(JDK1.8)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
public class TestStringTable {
//运行环境JDK1.8
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "a";
String s2 = "b";
String s3 = "a" + "b";
String s4 = s1 + s2;
String s5 = "ab";
String s6 = s4.intern();
//问
System.out.println(s3 == s4);
System.out.println(s3 == s5);
System.out.println(s3 == s6);
String x2 = new String("c") + new String("d");
String x1 = "cd";
x2.intern();
//问
System.out.println(x1 == x2);
String y2 = new String("e") + new String("f");
y2.intern();
String y1 = "ef";
//问
System.out.println(y1 == y2);
}
}
输出答案
展开查看
false
true
true
false
true 解析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
public class TestStringTable {
//运行环境JDK1.8
//代码运行时,常量池加载到运行时常量池中,还没有变为Java中的对象
//执行String s1 = "a"时,会把"a"加入到串池中(前提hash值不存在,存在则不增加)
//HashTable不能扩容,可通过虚拟机参数设置
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "a";
//串池 ["a"] s1为串池中"a"的地址
String s2 = "b";
//串池 ["a","b"] s2为串池中"b"的地址
String s3 = "a" + "b";
//此处编译优化,等价于 s3 = "ab"; 串池 ["a","b","ab"] s3为串池中"ab"的地址
String s4 = s1 + s2;
//使用StringBuild().append拼接,再通过new String()生成对象,所以 s4 = new String("ab");
String s5 = "ab";
//串池已存在"ab",s3为串池中"ab"的地址
String s6 = s4.intern();
//把 s4 = new String("ab"); 手动加入串池,由于串池已经存在"ab",所以失败,s4 = new String("ab");
//而s6为串池中"ab"的地址
//问
System.out.println(s3 == s4);//false
System.out.println(s3 == s5);//true
System.out.println(s3 == s6);//true
String x2 = new String("c") + new String("d");
//使用StringBuild().append拼接,再通过new String()生成对象,所以 x2 = new String("cd");
String x1 = "cd";
//串池 ["cd"] x1为串池中"cd"的地址
x2.intern();
//把 x2 = new String("cd"); 手动加入串池,由于串池已经存在"cd",所以失败,x2 = new String("cd");
//问
System.out.println(x1 == x2);//false
String y2 = new String("e") + new String("f");
//使用StringBuild().append拼接,再通过new String()生成对象,所以 y2 = new String("ef");
y2.intern();
//把 y2 = new String("ef"); 手动加入串池,由于串池不存在"ef",所以成功,串池 ["ef"],y2为串池中"ef"的地址;
String y1 = "ef";
//串池 ["ef"] y1为串池中"ef"的地址
//问
System.out.println(y1 == y2);//true
}
}
习题二(JDK1.6)
思考在JDK1.6环境下执行习题一代码
输出答案
展开查看
false
true
true
false
false 解析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
public class TestStringTable {
//运行环境JDK1.6
//代码运行时,常量池加载到运行时常量池中,还没有变为Java中的对象
//执行String s1 = "a"时,会把"a"加入到串池中(前提hash值不存在,存在则不增加)
//HashTable不能扩容,可通过虚拟机参数设置
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "a";
//串池 ["a"] s1为串池中"a"的地址
String s2 = "b";
//串池 ["a","b"] s2为串池中"b"的地址
String s3 = "a" + "b";
//此处编译优化,等价于 s3 = "ab"; 串池 ["a","b","ab"] s3为串池中"ab"的地址
String s4 = s1 + s2;
//使用StringBuild().append拼接,再通过new String()生成对象,所以 s4 = new String("ab");
String s5 = "ab";
//串池已存在"ab",s3为串池中"ab"的地址
String s6 = s4.intern();
//把 s4 = new String("ab"); 复制一份手动加入串池,由于串池已经存在"ab",所以失败,s4 = new String("ab");
//而s6为串池中"ab"的地址
//问
System.out.println(s3 == s4);//false
System.out.println(s3 == s5);//true
System.out.println(s3 == s6);//true
String x2 = new String("c") + new String("d");
//使用StringBuild().append拼接,再通过new String()生成对象,所以 x2 = new String("cd");
String x1 = "cd";
//串池 ["cd"] x1为串池中"cd"的地址
x2.intern();
//把 x2 = new String("cd"); 复制一份手动加入串池,由于串池已经存在"cd",所以失败,x2 = new String("cd");
//问
System.out.println(x1 == x2);//false
String y2 = new String("e") + new String("f");
//使用StringBuild().append拼接,再通过new String()生成对象,所以 y2 = new String("ef");
y2.intern();
//把 y2 = new String("ef"); 复制一份手动加入串池,由于串池不存在"ef",所以成功,串池 ["ef"],y2 = new String("cd");
String y1 = "ef";
//串池 ["ef"] y1为串池中"ef"的地址
//问
System.out.println(y1 == y2);//true
}
}
总结
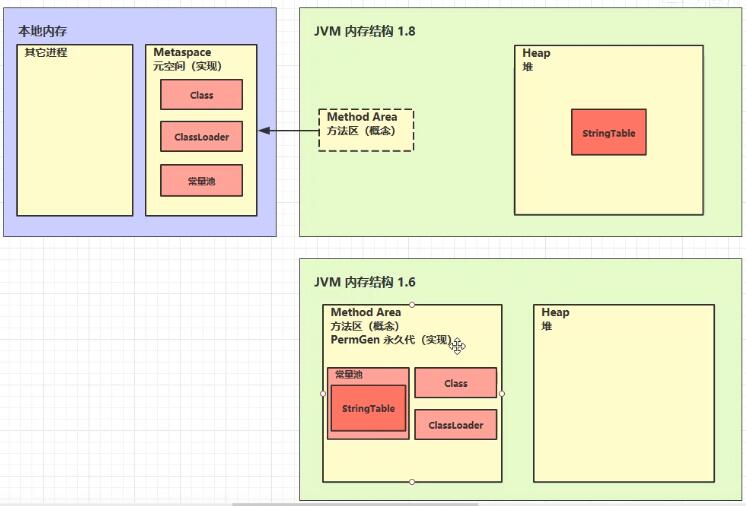
1、理解串池的概念和变量存放位置
2、在JDK6中data.intern()方法是复制一份data出来执行加入串池的操作,加入成功或失败都返回串池中的数据
3、在JDK8中data.intern()方法是直接data执行加入串池的操作,加入成功data指向串池中数据的地址,失败则对象不变,加入成功或失败都返回串池中的数据
4、JDK6串池用的永久代,JDK8串池用的堆空间
5、-XX:StringTableSize=1009 可以设置StringTable的桶个数,最小是1009